Yeast Protein: The Next Big Thing in Plant-Based Nutrition
In recent years, plant-based proteins have taken the health and fitness world by storm. Among the myriad options available, yeast protein is emerging as a powerhouse of nutrition. In this article, we’ll explore what yeast protein is, its nutritional benefits, how it compares to other protein sources, and how you can incorporate it into your diet.

What is Yeast Protein?
Yeast protein is derived from nutritional yeast, a deactivated yeast commonly used in food products for its savory, cheese-like flavor. Unlike brewer’s yeast or baker’s yeast, nutritional yeast is specifically grown for its nutritional content and is deactivated, meaning it won’t ferment or leaven food. Yeast protein is extracted and processed into a fine powder, making it a versatile ingredient for various culinary uses.
Nutritional Profile of Yeast Protein
Yeast protein is highly regarded for its impressive nutritional profile. A typical serving provides:
High-Quality Protein: Contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a complete protein source.
Rich in B Vitamins: Particularly B12, which is essential for vegans and vegetarians.
Minerals: Including iron, magnesium, and zinc.
Low in Fat and Calories: Ideal for weight management and muscle building.
The amino acid profile of yeast protein is comparable to that of animal proteins, making it an excellent alternative for those looking to reduce their meat intake without compromising on nutrition.
Health Benefits of Yeast Protein
Incorporating yeast protein into your diet can offer numerous health benefits:
Supports Muscle Growth and Repair: The complete protein profile helps in the maintenance and growth of muscle tissue.
Boosts Energy Levels: The B vitamins in yeast protein aid in energy metabolism.
Enhances Immune Function: Nutrients like zinc and selenium found in yeast protein are crucial for a healthy immune system.
Promotes Digestive Health: The fiber content in nutritional yeast supports a healthy digestive tract.
Aids Weight Management: Low in fat and calories, yeast protein can help you feel full longer, reducing overall calorie intake.
How to Use Yeast Protein
Yeast protein powder is incredibly versatile and can be easily incorporated into your daily diet. Here are some popular ways to use it:
Smoothies and Shakes: Blend it with fruits, vegetables, and your favorite plant-based milk.
Baking: Add it to bread, muffins, and pancakes for a protein boost.
Soups and Sauces: Stir it into soups, stews, and sauces for added nutrition.
Sprinkling: Use it as a topping for salads, popcorn, or pasta for a cheesy flavor and extra protein.
Yeast Protein vs. Other Protein Sources
When comparing yeast protein to other protein sources, several factors come into play:
Digestibility: Yeast protein is easily digestible, making it a suitable option for those with sensitive stomachs.
Allergen-Friendly: Unlike soy or dairy proteins, yeast protein is free from common allergens.
Sustainability: Yeast production has a lower environmental impact compared to animal farming.
Nutrient Density: Yeast protein often contains more vitamins and minerals compared to isolated plant proteins like pea or rice protein.
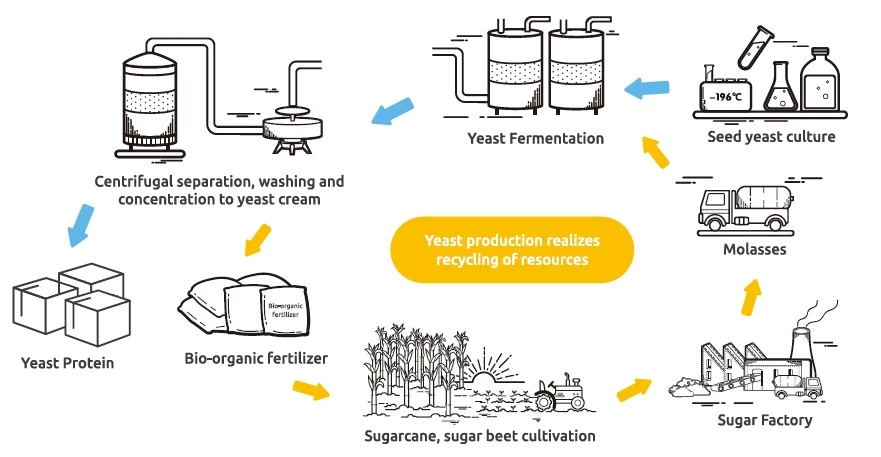
Yeast protein is a nutritional powerhouse that offers a complete protein profile, essential vitamins, and minerals, making it an excellent addition to any diet. Whether you’re looking to boost your protein intake, support muscle growth, or simply enjoy a sustainable and allergen-friendly protein source, yeast protein is worth considering. Incorporate it into your meals and enjoy the myriad health benefits it has to offer.
By highlighting the versatility and nutritional benefits of yeast protein, this article aims to provide a comprehensive guide that ranks well in search engines and serves as a valuable resource for readers interested in plant-based nutrition.
Source: NZ Protein
