The Remarkable Effects of Yeast Protein on Gut Health

Introduction
Yeast protein (YP) is increasingly recognized for its potential benefits in human nutrition. Derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, YP is a sustainable and efficient protein source with numerous health benefits. This article delves into the effects of YP on gut microbiota, comparing it with more commonly known proteins such as soybean protein isolate (SPI) and whey protein isolate (WPI). Understanding these impacts can help guide dietary choices and improve overall health.
Understanding Gut Microbiota
Gut microbiota comprises trillions of microorganisms living in our digestive tract. These microbes play a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, and even mental health. A balanced gut microbiota is essential for maintaining health, and dietary choices significantly influence this balance.
The Role of Dietary Proteins
Different proteins can affect gut microbiota composition and function in unique ways. Proteins are broken down into amino acids, which are then used by gut bacteria, influencing their growth and activity. Therefore, the type of protein consumed can promote or inhibit the growth of specific bacterial populations.
Benefits of Yeast Protein
Enhanced Gut Microbiota
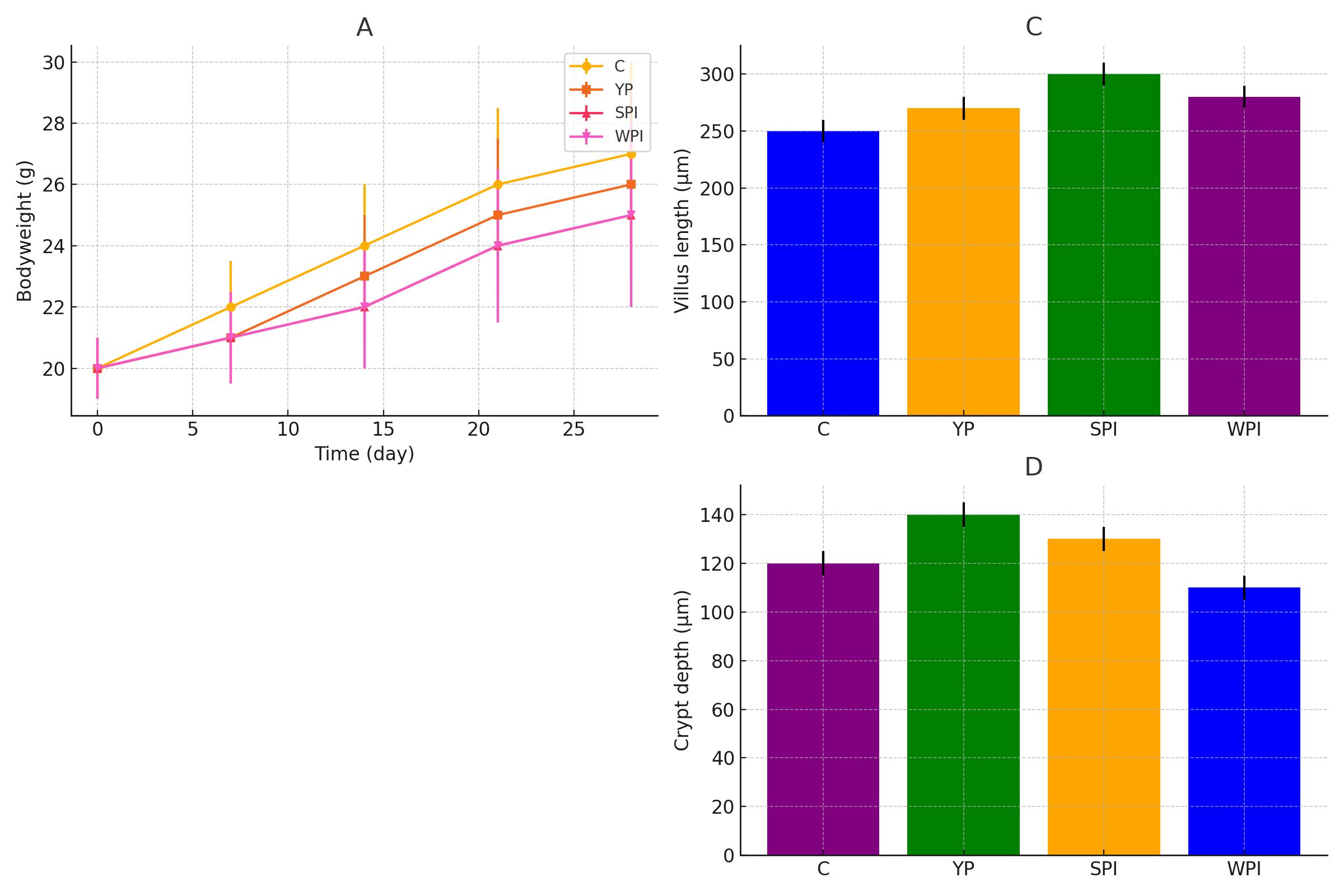
Studies have shown that YP supplementation can positively alter gut microbiota. It increases the population of beneficial bacteria such as Parabacteroides and Prevotella. These bacteria are known for their roles in breaking down complex carbohydrates, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), and supporting gut health.
Improved Intestinal Immunity
YP has been found to enhance intestinal immunity. It upregulates immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM, IgG) and anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10, while reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6. This modulation helps maintain a healthy immune response in the gut, preventing excessive inflammation and promoting tissue repair.
Antioxidant Properties
Antioxidants are vital for protecting cells from oxidative stress, which can lead to chronic diseases. YP increases the levels of glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), an essential antioxidant enzyme in the intestines. This boost in antioxidant activity helps mitigate oxidative damage, supporting overall gut health.
Yeast Protein vs. Other Proteins
Soybean Protein Isolate (SPI)
SPI is a widely used plant-based protein. While it is beneficial, it does not significantly enhance gut microbiota composition compared to YP. SPI's impact on gut bacteria is relatively neutral, making it less effective in promoting gut health than YP.
Whey Protein Isolate (WPI)
WPI is a popular animal-based protein, especially among athletes. However, it can sometimes promote the growth of potentially harmful bacteria if consumed excessively. In contrast, YP consistently supports beneficial bacteria, making it a healthier option for gut microbiota.
Practical Applications
Incorporating YP into the diet can be straightforward and beneficial. It can be added to smoothies, baked goods, or even sprinkled over meals. Given its favorable impact on gut microbiota and immune function, YP is particularly suitable for individuals looking to enhance their digestive health, boost their immune system, and increase their protein intake sustainably.
Broader Impacts on Health
Digestive Health
A balanced gut microbiota is crucial for optimal digestion. By promoting beneficial bacteria and enhancing immune function, YP supports efficient nutrient absorption and reduces gastrointestinal issues like bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
Immune System Support
The gut plays a significant role in immune function. YP's ability to upregulate immunoglobulins and anti-inflammatory cytokines strengthens the immune response, helping the body fight infections more effectively.
Metabolic Health
Gut health is closely linked to metabolic health. A healthy gut microbiota helps regulate metabolism, potentially reducing the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic disorders. YP, by supporting gut health, indirectly contributes to better metabolic outcomes.
Future Perspectives
The promising benefits of YP on gut health open up several avenues for future research and development. As the understanding of the gut microbiome deepens, YP could be tailored to target specific health issues. For example, it could be formulated to enhance gut health in individuals with specific conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Additionally, YP's sustainable production makes it an attractive option in the context of global food security. With the growing demand for protein sources and the environmental impact of traditional protein production, YP offers a viable alternative that is both health-promoting and eco-friendly.
Conclusion
Yeast protein stands out as a powerful dietary supplement with significant benefits for gut health. Its ability to enhance beneficial gut bacteria, improve intestinal immunity, and provide robust antioxidant support makes it an excellent choice for anyone looking to improve their overall health through diet. As research continues to uncover its full potential, YP is set to become a staple in health-conscious diets.
Source: MDPI - The Effects of Yeast Protein on Gut Microbiota in Mice.
